The goal of this article
The goal of this article is to extend the geography in 3D, including
- Polar coordinates: latitude and longitude
- Cardinal directions: north-south and east-west
into the imaginary planet in 4D.
Contents
- Sine and Cosine
- Euclidean space
- Stereographic projection
- Glome (Hypersphere)
- Hyperspherical coordinates
- Hopf fibration
- Hopf coordinates
Introduction
Most people have heard of terms to describe a location on Earth: Latitude and Longitude. These are in geography textbooks for middle school students. However, the description is somewhat vague. Not many people have clear images of how latitude and longitude work. In the book “Alice’s Adventure in Wonderland” by Lewis Carroll (1951), Alice mutters something like “Where am I now? In latitude and longitude?” when falling a rabbit hole, despite she barely knew what these terms mean.
In fact, latitude and longitude are defined using the trigonometric function. This is the concept in high school geometry, which explains why middle school geography never teaches it accurately.
Latitude and longitude are parameters in angles, which make coordinates to describe any location on a sphere like Earth. In this article, we learn the definition of the angles in the form of equations.
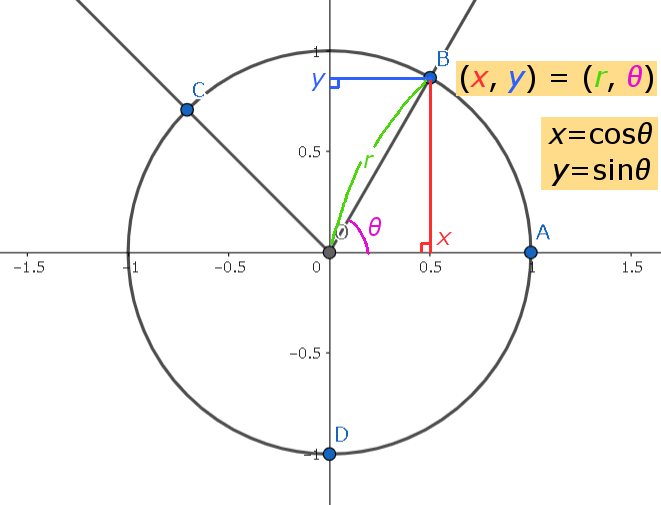
Circle
A circle is a closed curve every point of which is equally distant from a fixed point within it.
On the circle, one can move in only one direction; thus, one angular parameter between 0° & 360° can determine any location.
The point of \(\theta\) degrees is on \((\cos \theta, \sin \theta)\).
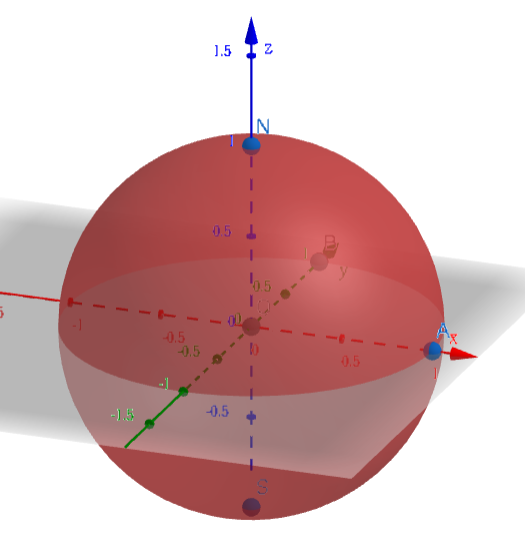
Sphere
Sphere: a solid figure so shaped that every point on its surface is an equal distance from the center.
The ends of the axis are called Poles.
The mid-section is called the Equator. It is an imaginary circle around the earth that is everywhere equally distant from the two poles.
The Prime Meridian is the line which connects both poles & crosses Greenwich, England. The city is chosen for historical reasons.
The surface of Earth is 2-dimensional manifold. That is, any location is expressed with two parameters, and one can move in two perpendicular directions. By defining positive and negative directions, we get four directions: north-south and east-west.
Directions on Earth
The direction to North Pole is called north. Its opposite direction is called south, and it is the direction to South Pole.
The direction of Earth's rotation on any point (except for the poles) is called east, & the opposite direction is called west. The speed of rotation varies from planet to planet.
Coordinates on Earth
Latitude is the angular distance north or south from the Equator measured in degrees.
Longitude is the angular distance east or west from the Prime Meridian.
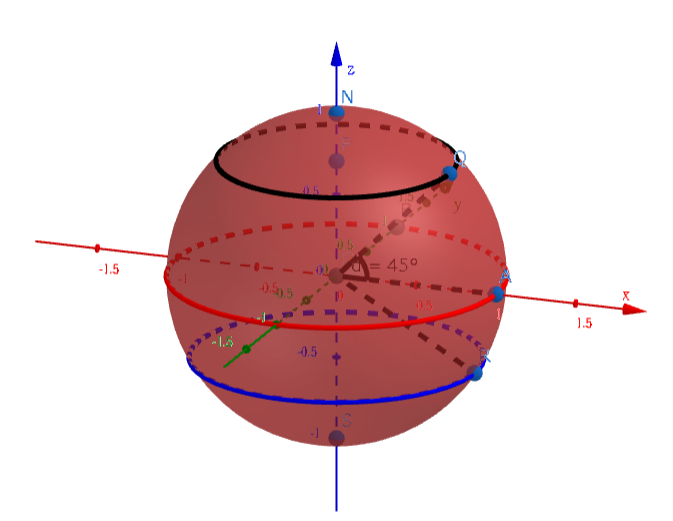
For convenience, we will consider the radius of the earth as 1, the axis of rotation as \(z\)-axis, & the intersection of equator & prime meridian as \((1,0,0)\).
North Pole is \((0,0,1)\); South Pole is \((0,0,-1)\). The equator is on \(xy\)-plane.
The black circle is latitude 45°. Its radius is \(\cos 45°\); it's on the plane \(z= \sin 45°\);
The red circle is the equator; the blue circle is latitude -30°.
Conversion
Generally, the point of \((Lat, Lon)\) is on \((\cos Lat \cos Lon, \cos Lat \sin Lon, \sin Lat)\).